Psychedelic mushrooms, also known as magic mushrooms, contain a variety of active compounds that contribute to their psychoactive effects. There are over 200 species of psychedelic mushrooms, and each contains a complex mix of compounds. Here’s a detailed look at the primary and lesser-known psychoactive components found in these fungi.
Primary Psychoactive Compounds
- Psilocybin: The most well-known psychoactive ingredient in magic mushrooms. Psilocybin is a prodrug that must be metabolized by the body. When ingested, it is converted into psilocin, the active form responsible for the psychedelic experience.
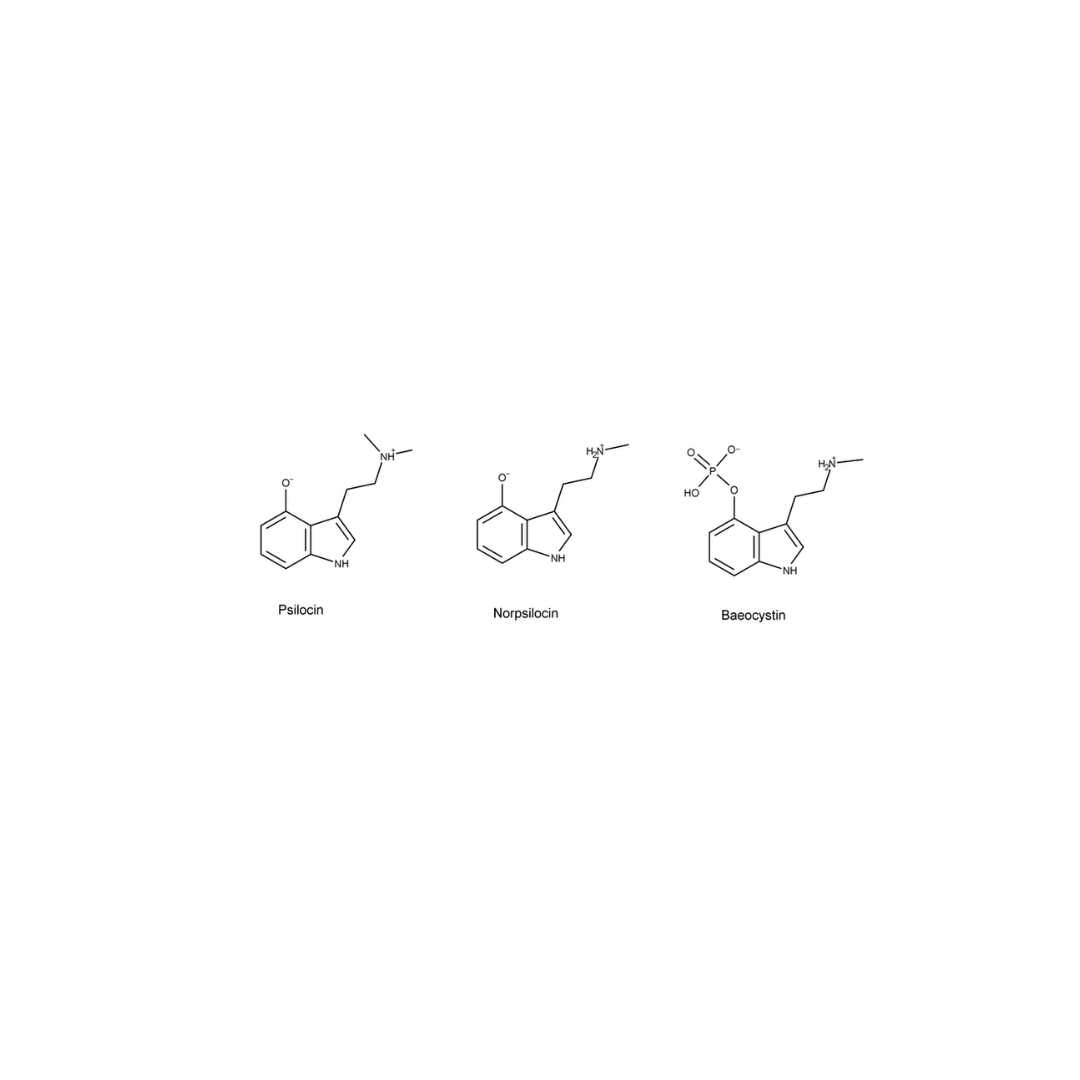
- Psilocin: The active compound resulting from the metabolism of psilocybin. Psilocin is directly responsible for the hallucinogenic effects experienced during a mushroom trip.
Other Notable Psychoactive Compounds
In addition to psilocybin and psilocin, several other tryptamines and related substances contribute to the effects of psychedelic mushrooms:
- Baeocystin: A compound found in certain species of magic mushrooms that may contribute to the overall psychoactive experience.
- Norbaeocystin: Similar to baeocystin, it is a minor psychoactive compound present in some mushrooms.
- Norpsilocin: A derivative of psilocin that also has psychoactive properties.
- Aeruginascin: A compound found in some psychedelic mushrooms that may influence the overall experience.
Norbaeocystin: Similar to baeocystin, it is a minor psychoactive compound present in some mushrooms.
Norpsilocin: A derivative of psilocin that also has psychoactive properties.
Unique Compounds in Amanita Muscaria
Amanita muscaria, or the fly agaric, is notable for its different psychoactive profile. Unlike other psychedelic mushrooms, it does not contain psilocybin or psilocin. Instead, its primary psychoactive compounds include:
- Muscimol: The primary compound responsible for the psychoactive effects of Amanita muscaria.
- Ibotenic Acid: A precursor to muscimol, contributing to the mushroom’s effects.
- Muscarine: Another active ingredient that affects the nervous system.
Conclusion
Psychedelic mushrooms are rich in a diverse array of psychoactive compounds. The primary components include psilocybin and psilocin, while additional compounds such as baeocystin, norbaeocystin, and aeruginascin also play a role in their effects. Furthermore, mushrooms like Amanita muscaria contain unique substances like muscimol and ibotenic acid, offering a different psychedelic experience.